Home > Mental care principles > #2 Therapies > Part 2: Types of therapies
#2 Therapies and Counseling
Part 2: Types of therapies

Introduction
A large variety of approaches exist in psychotherapy. Wikipedia, for example, identifies over 150 psychotherapies.
Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult for consumers to figure out which approach works best for their needs. The distinction among approaches is blurry and is differentiated mostly by philosophical roots, not necessarily by consumer needs.
According to the American Psychological Association, approaches to psychotherapy fall into five broad categories. [1]
- Psychoanalysis and psychodynamic therapies: Based on a theory about changing thoughts by exploring unconscious meanings
- Behavior therapy: Based on a theory about changing behavior by learning normal and abnormal behaviors
- Cognitive therapy: Based on a theory about changing thoughts by learning normal and abnormal thoughts
- Humanistic therapy: Based on a theory about respect and human capacity to make rational choices
- Integrative or holistic therapy: Blending elements from different approaches
-
[1] Different approaches to psychotherapy. American Psychological Association. Retrieved on May 27, 2016. Link
This is still a philosophical categorization and is not practical or useful for consumers. Instead of relying on dogmatic views, consumers should look at the practical purposes and features of psychotherapies. For that reason, we identify and discuss five therapy types:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT),
- Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT),
- Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT),
- Creative arts therapies (CAT), and
- Family counseling.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
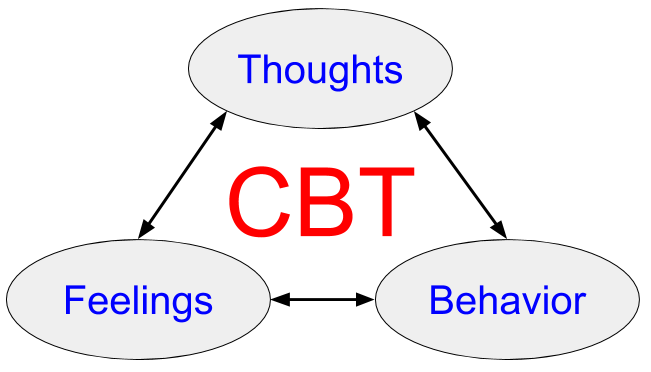
CBT is not a single therapy method; rather, it is a class of therapies that share the same principle—changes in thoughts can improve feelings and behavior. The exact procedure varies among therapists, but the general features can be highlighted as follows:
- CBT is goal-oriented. The process begins by identifying problematic feelings and behaviors.
- CBT is collaborative. The therapist and patient work together to find appropriate skills necessary to solve the problem.
- CBT requires homework. The patient must work to learn the necessary skills.
- CBT is short-term. Therapy may end in less than 20 sessions or 5 months.
CBT is commonly used to treat a variety of mental conditions such as depression, anxiety, addiction, and dependence. The good news for consumers is that CBT is prevalent, and many online resources are available to learn more about it.
- PsychCentral is a good starting place for learning about the basics of CBT. Link
- Wikipedia shows a list of CBT therapies. Link
- Explore with search keyword "cognitive behavioral therapy." Link
2. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
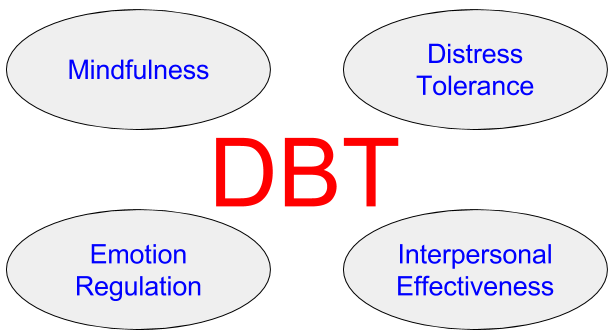
DBT is a special type of CBT originally developed by psychologist Marsha M. Linehan in the 1980s to treat suicidal individuals diagnosed with borderline personality disorder. Since then, DBT has been used to treat a variety of conditions, including depression, substance dependence, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
As the term "dialectical" implies, DBT emphasizes the integration of opposite strategies: acceptance and change. While change is the core strategy of CBT, DBT recognizes that some patients do not respond well to the forced change that CBT demands. DBT integrates the concept of acceptance from Buddhism as a way of preparation and acclimatization for patients to make progress toward eventual changes.
DBT uniquely teaches four sets of behavioral skills:
- Mindfulness: Learn to be aware of the present moment
- Distress tolerance: Learn to tolerate pain in difficult situations
- Emotion regulation: Learn to think differently
- Interpersonal effectiveness: Learn to communicate with self-respect
- The Linehan Institute has the most authoritative information about DBT. Link
- Explore with search keyword "dialectical behavior therapy." Link
3. Interpersonal Psychotherapy
IPT is a time-limited therapy that focuses on interpersonal issues. It aims to improve symptoms, interpersonal functioning, and social support in 6~20 sessions. It was originally developed in the 1970s by Gerald Klerman, Myrna Weissman, and Eugene Paykel to treat depression. Since then, IPT has been used for a variety of conditions, populations, and settings.
IPT appears to be more approachable than CBT for young people and older adults because it emphasizes relationships and requires less homework than CBT. In addition, IPT uses less technical words than other psychotherapies, making it more accessible to wider populations.
- WebMD has good, easy to digest information about IPT. Link
- Explore with search keyword "interpersonal psychotherapy." Link
4. Creative Arts Therapies (CAT)
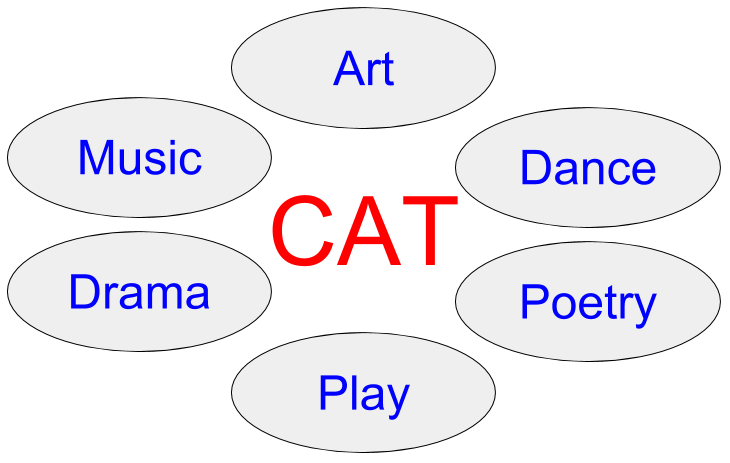
CAT (also called Expressive Therapies) is an umbrella term for a group of therapies that use creative, expressive, artistic activities as a remedy for mental conditions. Based on the principle that creative expression and imagination improve awareness of the body, feelings, and thoughts, CAT therapists use imagery, music, dance, movement, drama, poetry, storytelling, and visual arts in an integrated way to help patients heal or foster growth.
While most psychotherapies utilize a cognitive mode of action for healing, CAT is unique in its focus on sensory and physical modes. Consumers may find CAT a good alternative to classic talk therapies like CBT and IPT. The International Expressive Arts Therapy Association and National Coalition of Creative Arts Therapies Associations are promoting CAT worldwide and in the US, respectively.
- Psychology Today has a good summary of CAT. Link
- Explore with search keyword "creative arts therapy." Link
5. Family Counseling

Family counseling (or family therapy) is an important branch of psychotherapy that emphasizes relationships as an important factor in mental health. Although family counseling has a long history in various cultures, the contemporary therapeutic form originates from child guidance and marriage counseling in the early 20th century. Since then, the field evolved beyond the traditional family to include relationships among people who are not related by blood or marriage.
Like CBT and other psychotherapies, the exact method and procedure for family counseling differs among therapists. Some common features are:
- Short-term: The number of sessions may be between 5 and 20
- All members meet: Members of the family (or group) meet at the same time to observe habitual interaction patterns
- Less focus on cause-effect analysis: Rather than blaming individuals, therapists and patients work together to find ways to better the situation
- Mayo Clinic has a good summary of family counseling. Link
- Explore with search keyword "family counseling." Link
